The gas-load V-I curve, on the other hand, is generated during the normal operation of the
process while the ESP is energized. The procedure for generating the gas-load V-I curve is
the same as for the air load except that gas-load V-I curves are always generated from the
outlet fields first and move toward the inlet. This prevents the upstream flow that is being
checked from disturbing the V-I curve of the downstream field readings. Although such
disturbances would be short-lived (usually 2 minutes, but sometimes lasting up to 20 minutes),
working from outlet to inlet speeds up the process.
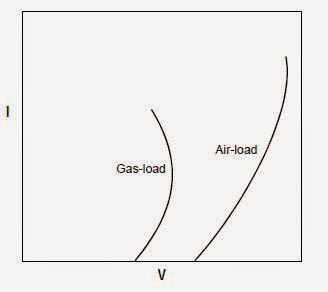
The curves generated under gas-load conditions will be similar to air-load curves. Gasload
curves will generally be shifted to the left however, because sparking occurs at lower
voltage and current when particles are present. The shape of the curve will be different for
each field depending on the presence of particulate matter in the gas stream (see
Figure
Also, gas-load curves vary from day to day, even minute to minute. Curve positions may
change as a result of fluctuations in the following:
• Amount of dust on plates
• Gasflow
• Particulate chemistry loading
• Temperature
• Resistivity
Nonetheless, they still should maintain a characteristic pattern. Gas-load curves are normally
used to isolate the cause of a suspected problem rather than being used on a day-today
basis; however, they can be used daily if necessary.
process while the ESP is energized. The procedure for generating the gas-load V-I curve is
the same as for the air load except that gas-load V-I curves are always generated from the
outlet fields first and move toward the inlet. This prevents the upstream flow that is being
checked from disturbing the V-I curve of the downstream field readings. Although such
disturbances would be short-lived (usually 2 minutes, but sometimes lasting up to 20 minutes),
working from outlet to inlet speeds up the process.
The curves generated under gas-load conditions will be similar to air-load curves. Gasload
curves will generally be shifted to the left however, because sparking occurs at lower
voltage and current when particles are present. The shape of the curve will be different for
each field depending on the presence of particulate matter in the gas stream (see
Figure
Comparison of typical air-load and gas-load
V-I curves
Also, gas-load curves vary from day to day, even minute to minute. Curve positions may
change as a result of fluctuations in the following:
• Amount of dust on plates
• Gasflow
• Particulate chemistry loading
• Temperature
• Resistivity
Nonetheless, they still should maintain a characteristic pattern. Gas-load curves are normally
used to isolate the cause of a suspected problem rather than being used on a day-today
basis; however, they can be used daily if necessary.















0 comments:
Post a Comment